We were asked to analyse one axle overload offence and propose options to prevent similar situations in future. We applied TruckLoader, breaking the task into the following stages:
- Model loading, as a result of which a fine was imposed for exceeding the axle load.
- Determine the possibility of carrying out the same loading without axial excesses.
- Determine the likelihood of reloading additional pallets into the lorry.
Initial data for analysis:
- The protocol of offence and the waybill
- Tractor unit Scania + semi-trailer Schmitz
- 29 Euro pallets, gross weight of one pallet: 740 kg

Taking the data on the vehicle from the TruckLoader database, we modelled axle loads. We then compared them with the measurements obtained whilst weighing to replicate the cargo allocation during that transportation. The data perfectly coincided with the recorded overload on the second axle.
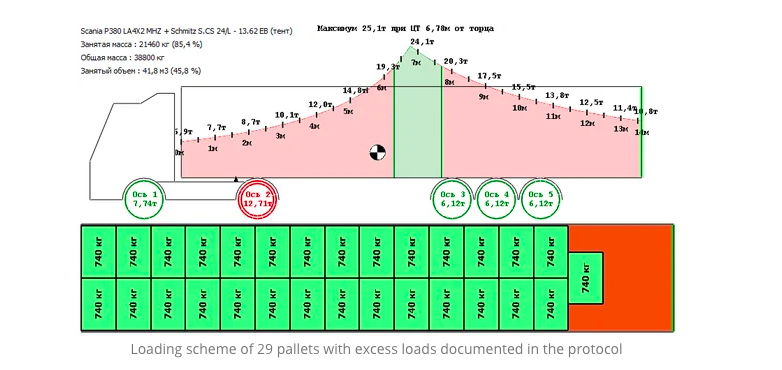
Next, we try to rearrange these pallets to avoid axle overload. Finally, we run TruckLoader in Balance mode, and it selects the best pallet allocation without axle overload.

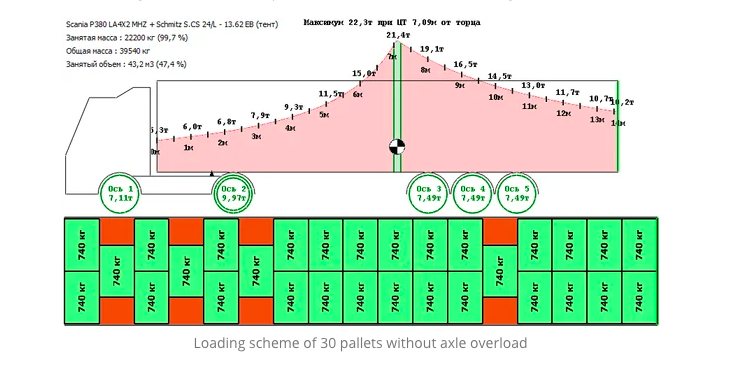
As we can see, a solution for 30 pallets was found even for reduced axial limits. Thus, you can carry an order that is heavier than the original without fines.
Conclusion:
To analyse the case, we simulated 3 LGV container loading options for the selected vehicle. We showed that using the TruckLoader algorithm, it is possible to plan the loading of vehicles without exceeding the axle loads while increasing the number of products transported.
The following video shows how TruckLoader works for analysing this case. Would you please turn on subtitles in your preferred language?